What are the parts of a guitar?
Author: Allan Kumpulainen Date Posted:July 21, '16
If you've been searching for a guitar to buy, you've probably been overwhelmed with talk of "locking tuners", "C-shape necks", "bone nuts" etc. So if you're struggling to sort between the things that are important to you on a new guitar, and specifications that don't matter, read on to decode all the parts of an acoustic, classical, and electric guitar, or scroll to the bottom for some helpful diagrams
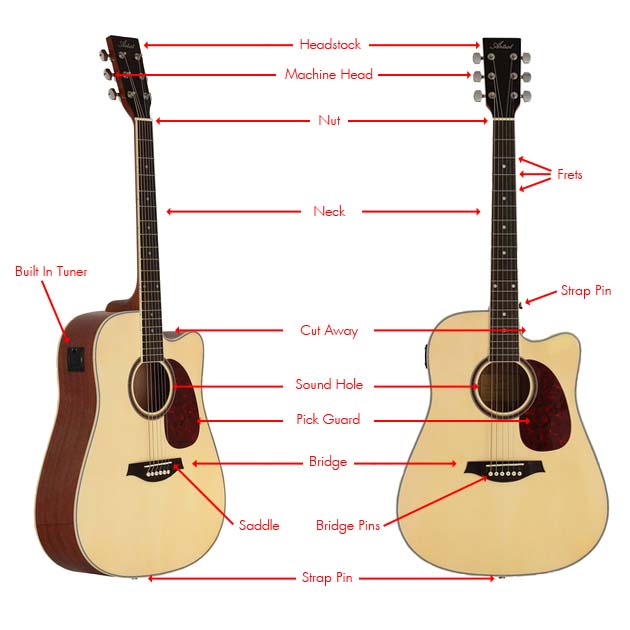
Guitar Parts Explained:
Headstock: Houses the machine heads for adjusting the tension (tuning) of the strings
Machine Head: Gear mechanism for tensioning (tuning) the guitar strings.
Nut: The white section that the strings run through, between the neck and the headstock. The nut on a beginner guitar is usually made from molded plastic. Higher grade guitars are made from bone.
Neck: This is where the strings run so that you can press your fingers down to change the pitch of the strings
Frets: The frets are small bumps in the neck which when a string is pressed against them makes a specific note. These are spaced very precisely to create a chromatic scale.
Built-in Tuner: All Beginner Artist Guitars include a built-in tuner. This means you'll never be without a tuner, where ever you go! Very simple to use. Check out our video guide on how to use this.
Strap Pin: Used to connect your strap (also included with Beginner Artist Guitars).
Cut Away: A section of the body that is "cut out" on the under side of the neck. This allows your fret hand to reach the higher frets more easily.
Sound Hole: The hole in the body that lets the sound escape from the body cavity. This is what gives the guitar its volume and warmth.
Pick Guard: Protects the surface of the guitar from scratches when strumming the guitar. These can be easily removed and swapped for a different colour if you would like to personalise your guitar. Check out our blog on how to do this.
Bridge (Acoustic Guitars): A solid piece of wood that is glued to the body of the guitar to handle the tension of the strings. The strings go through the bridge and into the body of the guitar. They're secured with bridge pins.
Bridge (Electric Guitars): Similar to Acoustic guitars but made from metal. There are many variations of the electric guitar bridge but all serve the same purpose of anchoring the strings.
Saddle: Similar to the nut, this is the contact point for the strings before they are secured to the bridge. Beginner models are made from plastic, higher grade guitars can be made from bone.
Bridge Pins: Used to secure the strings into the bridge of the guitar. Use a Bridge Pin Puller, pliers or even a spoon to remove if you need to replace your strings. Check out our string-changing guide!
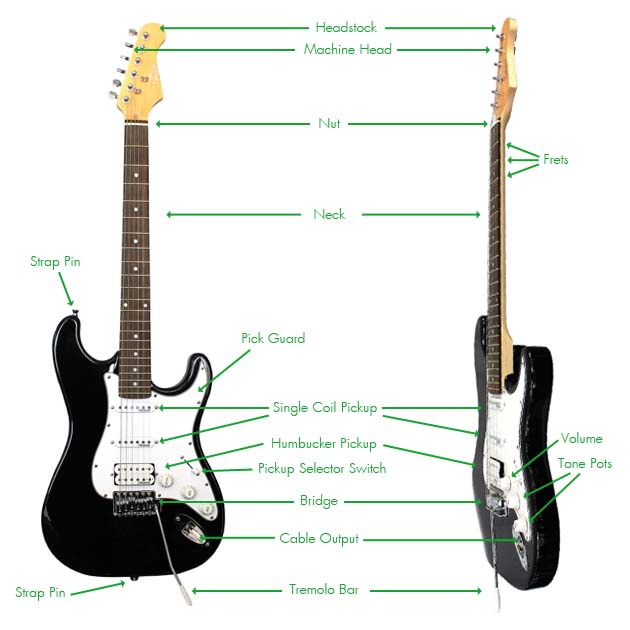
Specific to the AS1 Beginner Electric Guitar:
Single Coil Pickup: Converts magnetic energy of the vibrating strings into electric energy. This electrical current travels out of the guitar output through a cable into an amp.
Humbucker Pickup: A different type of pickup that reduces the amount of noise generated from overdriving your sound.
Pickup Selector Switch: This allows you to choose between pickups or a combination of two at a time. There are 5 options on a standard strat style guitar.
Volume: Allows you to control the output volume of the guitar.
Tone Pots: Control the tone, similar to a tone pot, or bass/treble on your home stereo.
Tremolo Bar: Allows you to move the bridge backward and forward, loosening or tightening the strings. This will bend the note up or down in pitch.
If you would like more information on choosing the right guitar for you, then feel free to email us, give us a call or click the live chat button below.
